Introduction
Enclosure is a fundamental component in modern industrial, electronic, and architectural uses, serving crucial protection and confinement for numerous systems and components. Metals Engineering is committed to offering excellent enclosure solutions designed and developed to serve the toughest demands in a broad spectrum of industries.
An enclosure, in the most general sense, is a protective assembly that is meant to surround sensitive equipment, components, or systems and protect them from environmental influences, physical stress, unauthorized access, and other hazards. Protective housings are the all-important interface between valuable internal components and the outside world, and they provide maximum performance and long life.
Our enclosures are available across a range from electrical cabinets, control panels, equipment enclosures, junction boxes, and special containment systems. Each is carefully designed with utmost care for material characteristics, ambient conditions, accessibility needs, and regulatory requirements. No matter what material they are made of – high-quality metals, high-performance polymers, or composite materials – our enclosures provide rugged protection that upholds the integrity of your mission-critical assets.
What is an Enclosure?
It is a protective cover or casing used to house, protect, or isolate something from environmental influences. It could be as simple as fencing around a property or an intricately designed housing unit for electronic components.
Types of Enclosures
1.Industrial Enclosures
It is applied in manufacturing and engineering. they are used for the protection of machines and equipment from the adverse effects of dust, moisture, and temperature.
Applications:
- Electrical panels
- HVAC systems
2. Property
Property fences, walls, or hedges mark boundaries and boundaries and provide security and privacy to homes, businesses, or farms.
Examples:
Chainlink fences, wooden fences, or stone walls.
3.Enclosures in Technology
it play a crucial role in electronics and IT in housing parts like servers, routers, and other sensitive equipment.
Function:
Protect against dust, heat, and unauthorized access.
4.Legal and Historical Enclosures
History will define as fencing public land in order to make it private. In this phase, land ownership and agricultural activities are significantly changed.
5.Electrical Enclosures
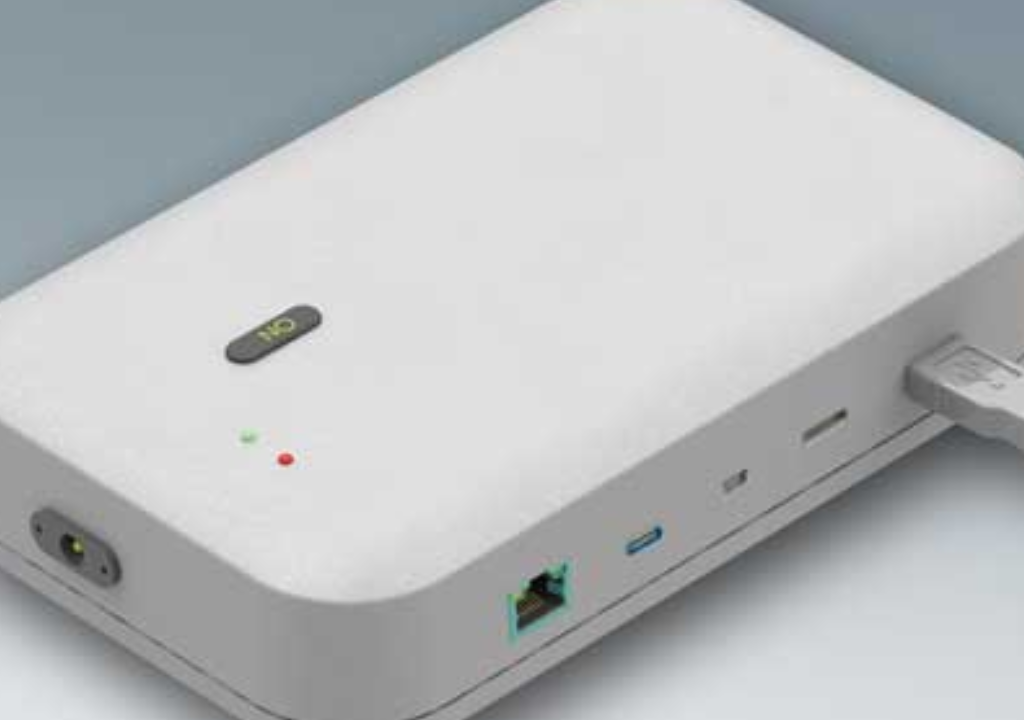

These are the pulse of electrical systems. They safeguard electrical hazards, in a manner of speaking. These serve as fortresses for complex electrical networks from environmental threats and possible damage.
6.Mechanical Enclosures
6.Mechanical Enclosures
Mechanical enclosures are a closed range of protection enclosures particularly created to envelop, accommodate, and act as mechanical parts, moving parts, and related systems. The carefully produced frames are the most essential in most mechanical uses for industrial, manufacturing, and engineering purposes. electrical enclosures are mostly produced to safeguard electronic components, mechanical enclosures are made with the particular challenges of mechanical systems in mind, including:
Structural Integrity: Prevention against excessive support of moving components and mechanical loads
Vibration Management: Reduction of vibration transfer to nearby equipment
Precision Alignment: Sustenance of critical tolerances of interfacing mechanical components
Lubrication Containment: Prevention from leakage of lubricants and hydraulic fluid
Thermal Management: Allowance for effective dissipation of heat from mechanical processes
Noise Reduction: Containment or dampening of noise operation
Guarding against Safety: Prevention of accidental contact with moving parts
Benefits of Enclosures
•Protection: Guard against mechanical damages, external conditions, and unauthorized entry.
•Organization: Keep things inside with well designed, organized structures.
•Safety: Provide less exposure to humans and their assets like animals and equipment for risky factors.
•Aesthetics: Add beauty to the space with attractive designed boundaries.
Selecting a Suitable Enclosure
purpose:
Determine what you want the to serve for, be it safety, protection, or organization.
Material:
Choose on strength, weatherability, and aesthetic appeal.
Tailored:
Look for it that are designed specifically to your needs, especially for industrial or technology applications.
Understanding Enclosure Fundamentals
they are like the silent guardians of technology, industry, and infrastructure keeping things safe, secure, and functioning perfectly.
Definition and Core Concepts
it is not just a box or a container. It’s actually a sophisticated protective system intended to shield, contain, and optimize whatever it protects. Think of it as advanced armor for machinery, electronics, and critical infrastructure.
Historical Evolution of Enclosure Technology
From primitive protective coverings to today’s smart, integrated systems, they have gone a long way. Envision moving forward in time and seeing how human ingenuity has transformed these protective solutions.
Environmental Enclosures
Weather Resistant Designs
Ever see equipment that could survive hurricanes, extreme heat, or freezing temperatures? This is the magic of advanced environmental.
Specialty Environmental Protections
Chemical resistant designs, dustproof systems are some of the designed for special and demanding environmental conditions.
Design Principles of Effective Enclosures
Material Selection
Picking the right material is like casting the perfect actor for a movie role. Each material brings unique properties:
- Stainless steel for corrosion resistance
- Polycarbonate for light weight protection
- Aluminum for thermal management
- Special composite materials for specific usages
Structural Integrity Factors
it does more than simply stop unwanted penetrationit bears upon performance, thermal flow control, and reliability matters that persist.
Design and Engineering Details
Load Capability
What load can one assume that an shall take? That is roughly akin to how much baggage can the superhero carry along with himself. Advanced engineers come to such critical estimations.
Thermal Management
Heat is the silent killer of electronic systems. Strategic design manages temperature, preventing performance degradation and extending equipment life.
Application Domains
Industrial Manufacturing
From automotive to aerospace, it play a vital role in protecting complex manufacturing systems and sensitive equipment.
Technology and Electronics
Smartphones, data centers, telecommunications – modern technology depends on sophisticated solutions to maintain performance and reliability.
Agriculture and Environmental Solutions
Specialized are required to withstand extreme outdoor conditions for precision agriculture, environmental monitoring, and research.
Advanced Technologies
Smart Systems
Something that protects and communicates. that self diagnoses. Something that adapts.
Integration with IoT
With Internet of Things, they are no longer passive protection shells but active, smart systems that provide real time data and insights.
Customization and Specialized Solutions
Industry Specific Designs in Enclosures
No industry is the same, and their needs are not, too. Customization would be the key to all unique protective needs.
Emerging Technological Trends
3D printing, nanotechnology, and advanced materials are pushing the limits of what is possible in enclosure design.
Economic and Strategic Considerations
Cost Effectiveness Analysis
Investment in the right is not a cost but a strategic move, which will prevent the risk of costly failure and increase equipment life.
Performance Optimization Strategies
The selection of the right is about protection, performance, and economical considerations.
Diagnostic and Predictive Maintenance
today have evolved into advanced diagnostic devices, ensuring proactive maintenance and optimization of performance.
FAQs
1. What makes a good enclosure design?
Material selection, thermal management, environmental adaptation, and specific usecase optimization.
2. How do enclosures affect equipment performance?
They protect against environmental hazards, control thermal environments, and prevent any loss of performance.
3. Are custom enclosures worth it?
For specific or high risk applications, the custom will surely reduce longterm operational risks and costs.
4. How is the enclosure changing with the advancement of technology?
IoT, smart diagnostic systems, and advanced materials are driving the innovation of it.
5. Can be sustainable?
Yes, through material selection and energy efficient designs and lifecycle considerations.
| Era/Period | Development and Use of Enclosures |
|---|---|
| Prehistoric Times | Early humans used natural barriers like caves or rock formations as protective. |
| Ancient Civilizations | Stone walls and wooden fences were built to secure livestock, homes, and agricultural lands. |
| Medieval Era | Castles and fortifications served as enclosures for defense and protection of communities. |
| 16th-18th Century | The Movement in Europe transformed common lands into private property for agriculture. |
| 19th Century | Industrial Revolution led for machinery and equipment in factories. |
| 20th Century | Development of technological for electrical panels, servers, and sensitive devices. |
| 21st Century | Modern are highly customized, with advanced materials used in industries, technology, and design. |
Conclusion
They represent strategic assets that safeguard, optimize, and enable technological and industrial progress. It is more than just being a barrier carry out critical functions in protection, organization, and security within and across industries. Be it to guard animals, house technology, or protect property, the make sure that functionality and efficiency are achieved. Investing in an appropriate can promote safety, extend the lifespan of equipment, and make overall productivity better. Take advantage of your needs now with a bespoke solution and enjoy the benefits of structured, secure environments.
Read more about our services at Red Craft Industry. your trusted source for top-quality solutions.


